Time of Flight Diffraction
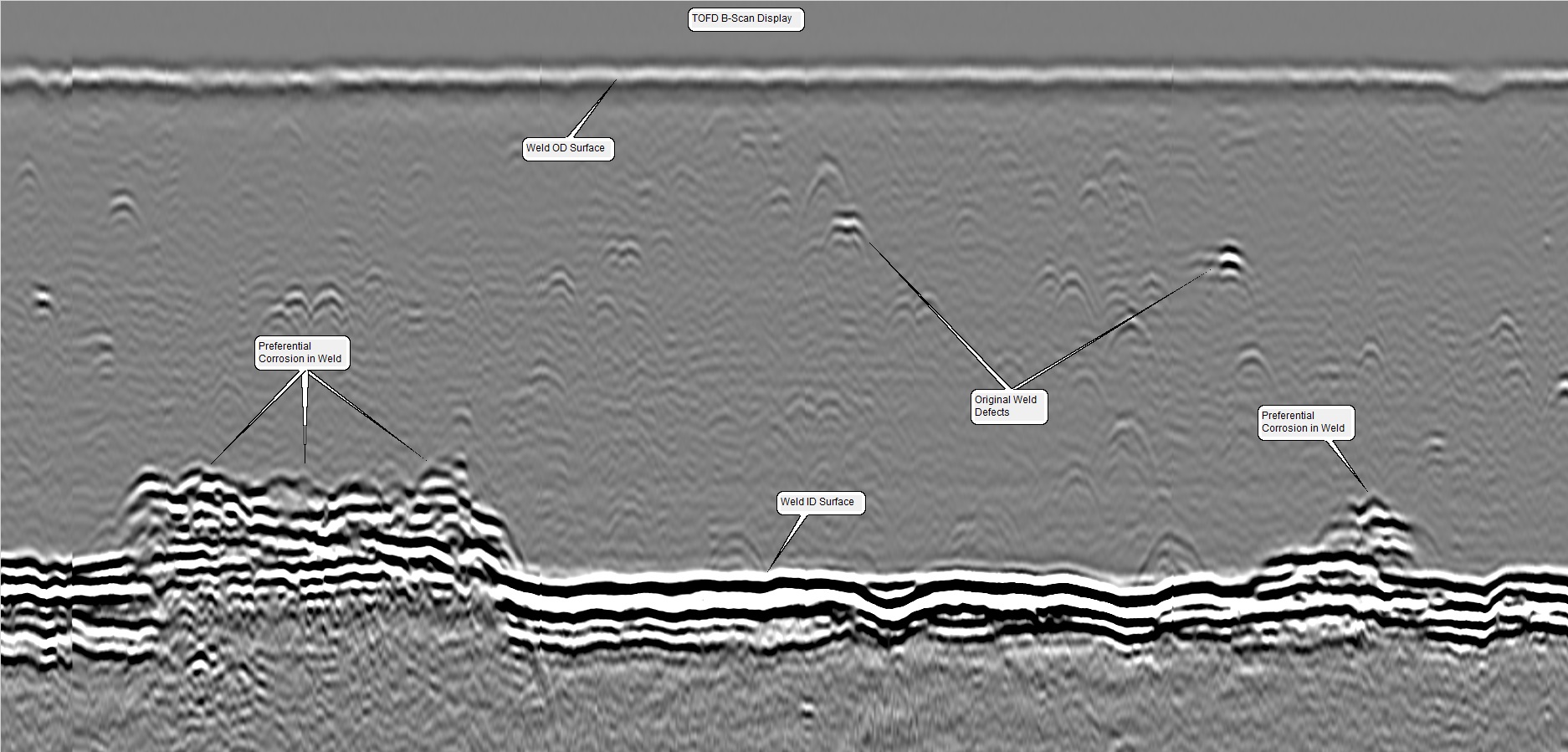
Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) is an ultrasonic testing method that utilizes a pair of transducers fixed opposite one another and centered over an area of interest such as welds.
One probe is used as the transmitter and the other as a receiver. The time of arrival of the ultrasonic beam reflecting off the back of the component is then measured. Diffraction occurs when the ultrasonic beam comes into contact with discontinuities such as cracks or weld defects.
The time of arrival of diffracted signals are then measured against the reflected signals from the back of the component. The TOFD method creates a complete picture of the weld or area of interest.
TOFD is most often used in conjunction with Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT) as a supplementary technique although it may be used on it’s own for various applications such as weld preferential corrosion. The main advantages to using TOFD is it’s high degree of precision and repeatability.
Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT) is an advanced non-destructive testing method utilizing a series of elements in a single transducer housing. The elements are pulsed using computed time delays allowing the ultrasonic beam to be steered in a desired direction and focused at a desired depth. PAUT is commonly used for weld inspection, crack detection and sizing, volumetric inspection of larger components such as forgings and castings, and corrosion mapping.
Fully Automated or Semi-Automated
Ultrasonics Testing
INDUSTRY SECTORS SERVED

